Preventing Common Sports Injuries: A Guide to Staying Active and Injury-Free
Sports play a crucial role in promoting physical fitness, mental well-being, and social interaction. Whether you’re a professional athlete or someone who enjoys staying active, injuries can be a frustrating obstacle. Fortunately, with the right precautions, many common sports injuries can be avoided.
Understanding Sports Injuries
Sports injuries encompass various physical conditions that occur during physical activity. They typically result from overuse, direct impact, or excessive force on the body. While no athlete is immune to injuries, awareness and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risks.
Common Sports Injuries and How to Prevent Them
1. Strains and Sprains
Strains involve overstretching or tearing of muscles or tendons, while sprains affect ligaments. These injuries often occur in high-movement sports like basketball and football. To prevent them, maintain muscle flexibility through regular stretching and warm-up exercises.
2. Groin Strain
Common in sports requiring sudden directional changes, groin strains can be severe. Proper stretching, warm-ups, and strength training exercises help reduce the risk. If injured, follow the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) and take anti-inflammatory medications as needed.
3. Achilles Tendonitis
This condition affects the Achilles tendon, connecting the calf muscles to the heel. It often results from overuse and poor stretching habits. Preventive measures include calf-strengthening exercises and proper stretching routines.
4. Shin Splints
Affecting runners and high-impact athletes, shin splints cause pain along the shinbone due to excessive stress on the muscles. Proper footwear, gradual activity progression, and shock-absorbing insoles can help prevent this condition.
5. Concussions
Common in contact sports like football and hockey, concussions result from head impacts. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and nausea. Wearing protective helmets and practicing proper techniques help minimize the risk.
6. Fractures and Dislocations
Fractures (broken bones) and dislocations often occur in high-velocity or contact sports. Strength training and using appropriate protective gear can help prevent these injuries.
7. Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow
Overuse injuries like tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow affect the elbow and forearm due to repetitive motions. Prevention includes using proper technique, appropriate equipment, and strengthening forearm muscles.
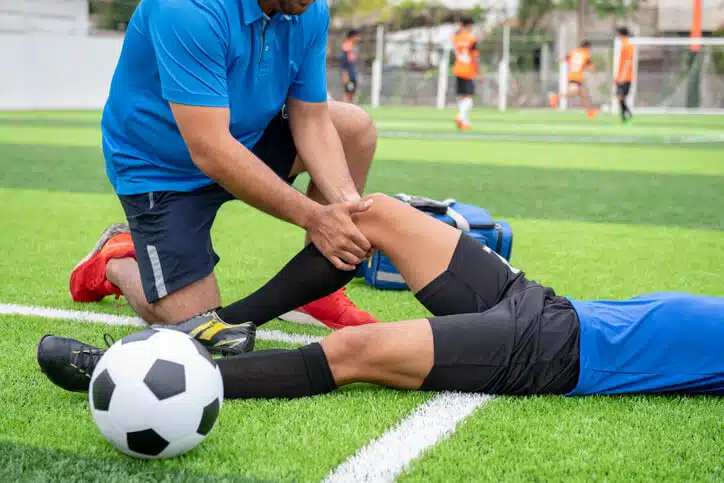
8. Knee Injuries
Knee injuries, such as ACL tears and meniscus damage, are common in soccer and basketball. Strength training and learning proper landing and pivoting techniques can help reduce knee injury risks.
9. Shoulder Injuries
Frequent in sports involving overhead motions, shoulder injuries can be prevented with proper stretching and strengthening exercises.
10. Ankle Sprains
Sudden twists or turns during sports can cause ankle sprains. Strengthening the ankle, wearing supportive footwear, and using braces or taping techniques can help prevent sprains.
Injury Prevention Strategies
1. Flexibility and Stretching
Incorporate daily stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce muscle strain risks. Post-activity stretching enhances recovery and injury prevention.
2. Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
Warming up gradually increases circulation, while cooling down helps muscles recover. A light jog or dynamic stretching before playing prepares the body for action.
3. Proper Gear and Footwear
Using sport-specific protective gear, including helmets, knee pads, and correctly fitted shoes, can prevent injuries. Ill-fitting equipment increases injury risks.
4. Strength Training and Conditioning
Strengthening core, leg, and upper body muscles enhances joint stability and reduces injury risks. Targeted workouts help prevent knee, shoulder, and back injuries.
5. Correct Technique and Form
Improper form leads to excessive strain on muscles and joints. Athletes should work with coaches to master the correct techniques for their respective sports.
6. Nutrition and Hydration
A balanced diet fuels the body for peak performance. Staying hydrated prevents muscle cramps and overheating, reducing injury risks.
7. Gradual Progression
Avoid overtraining by gradually increasing workout intensity. Pushing too hard too soon can lead to overuse injuries.
8. Rest and Recovery
Rest days allow muscles to repair and prevent overuse injuries. Athletes should prioritize sleep and recovery techniques to maintain peak performance.
9. Medical Consultation and Rehabilitation
Persistent discomfort should be evaluated by medical professionals. Regular check-ups and rehabilitation programs help prevent chronic injuries.
Conclusion
Sports injuries can disrupt an active lifestyle, but most can be prevented through proper preparation, training, and recovery. Athletes should listen to their bodies, practice injury prevention strategies, and seek medical guidance when needed. By taking the right precautions, you can continue enjoying sports safely and effectively for years to come.