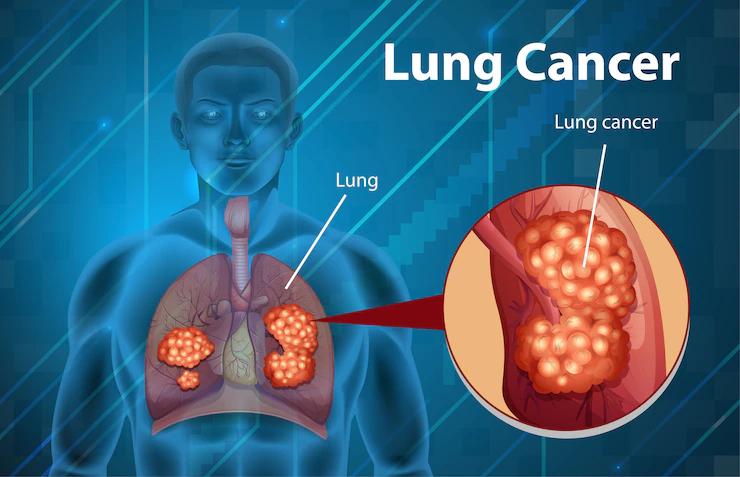
Lung Cancer: A Silent Threat
Lung cancer occurs when there is uncontrolled cell division or tumor formation in the lungs, leading to the destruction of healthy lung tissue and loss of function. The most concerning aspect of lung cancer is that it often goes unnoticed in its early stages. By the time symptoms appear—such as wheezing, breathlessness, persistent cough, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), or hoarseness—the disease may have already progressed to an advanced stage.
Common Causes of Lung Cancer in Non-Smokers
Contrary to common belief, lung cancer is not limited to smokers. Increasingly, non-smokers are being diagnosed with the disease due to a variety of environmental and genetic factors. Exposure to harmful substances like asbestos, radon, and air pollution plays a major role. Chronic lung conditions like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) further increase the risk. Alarmingly, secondhand smoke has become a significant contributor, affecting even children and young adults. Studies have shown that prolonged exposure to polluted air leads to blackened lung deposits, making once-healthy lungs a rarity.
How COPD Increases the Risk of Lung Cancer
COPD and lung cancer share a common factor: oxidative stress. Our bodies naturally produce free radicals, which contribute to aging and cell damage. However, when combined with environmental triggers like smoking and pollution, oxidative stress accelerates tissue damage and increases cancer risk. Research indicates that individuals with COPD are significantly more likely to develop lung cancer due to chronic inflammation and weakened immune responses.
The Hidden Dangers of Secondhand Smoke
While smoking is a well-known cause of lung cancer, secondhand smoke exposure is just as dangerous. There is no “safe level” of exposure—breathing in tobacco smoke can damage lung cells, weaken immunity, and increase the likelihood of cancer. The effects are particularly severe in children, leading to asthma, low birth weight, and even Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). Long-term exposure also raises the risk of strokes, heart disease, and reproductive issues in non-smokers.
Preventive Measures for Lung Cancer in COPD Patients
Although the risk of lung cancer remains high in COPD patients, adopting a proactive approach can significantly reduce it. Preventive measures include:
- Avoiding Smoking: Quitting smoking lowers the risk of lung cancer by more than 50%.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Eating antioxidant-rich foods and staying hydrated can support lung health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves cardiovascular health and lung function.
- Environmental Awareness: Limiting exposure to pollutants such as asbestos, radon, and industrial fumes.
- Routine Health Screenings: Individuals with a family history of lung disease should undergo regular check-ups to detect abnormalities early.
Conclusion
The connection between COPD and lung cancer is undeniable, yet researchers are still uncovering the exact mechanisms behind this link. What is clear, however, is the need for early detection, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions. Patients can benefit from oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and even lung transplants in severe cases. Vaccinations against respiratory infections can further help reduce complications. Staying vigilant, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking professional medical guidance can go a long way in preventing and managing lung-related diseases.
At The Ethics Multispeciality Hospital, we are committed to providing expert care for respiratory health. If you or a loved one is experiencing persistent lung-related symptoms, consult our specialists for a personalized treatment plan. Early intervention can save lives!